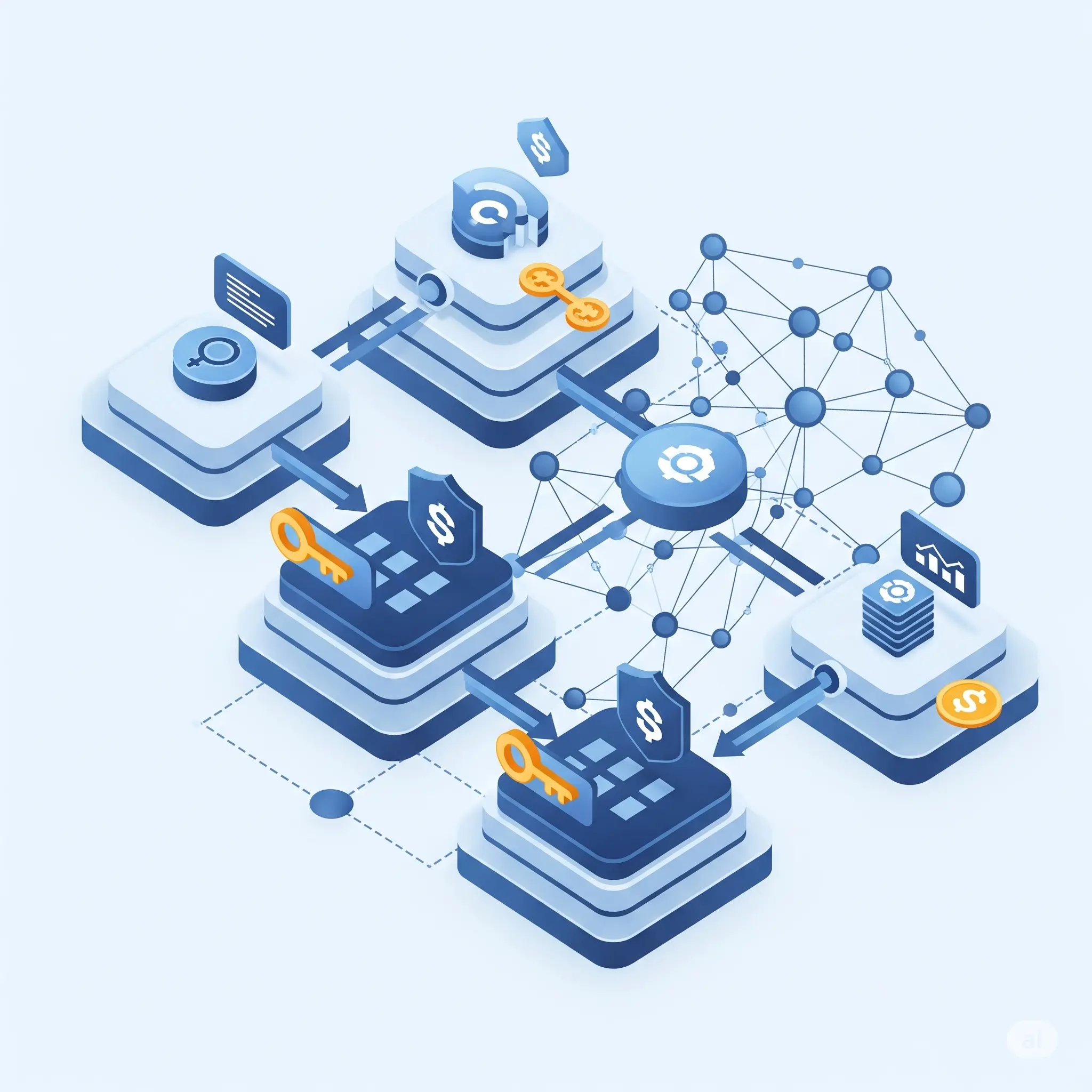
Blockchain, often hailed as the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is far more than just a digital ledger for financial transactions. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed, and immutable ledger system that records transactions across many computers.
How Does it Work? The Building Blocks of Trust
Imagine a digital chain where each "block" contains a list of transactions. Once a block is filled, it's linked to the previous block, forming a chronological chain.
Decentralization: Unlike traditional systems where a central authority (like a bank) maintains the ledger, blockchain distributes copies of the ledger across a vast network of computers (nodes).
This means no single entity has control, making it incredibly resistant to censorship and single points of failure. Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on a block and added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted.
Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, meaning any attempt to tamper with an earlier block would invalidate all subsequent blocks, immediately alerting the network. This creates an unchangeable and verifiable record. Cryptography: Advanced cryptographic techniques secure each transaction and link the blocks.
This ensures the integrity and authenticity of the data, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to manipulate information. Consensus Mechanisms: For a new block to be added to the chain, the majority of the network's participants must agree on its validity through various consensus mechanisms (like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake).
This democratic validation process further enhances security and prevents fraudulent entries.
Beyond Bitcoin: Real-World Applications
While blockchain's origins are deeply intertwined with cryptocurrencies, its potential applications stretch across a multitude of sectors:
Supply Chain Management: Track products from origin to consumer, ensuring authenticity, ethical sourcing, and reducing counterfeiting.
Imagine knowing exactly where your food comes from or proving the genuine origin of luxury goods. Healthcare: Securely manage patient records, streamline data sharing among healthcare providers, and ensure the integrity of clinical trial data.
Voting Systems: Create more secure, transparent, and verifiable elections, potentially increasing public trust in democratic processes.
Intellectual Property Rights: Protect copyrights and patents by providing an immutable timestamp and proof of ownership for creative works.
Real Estate: Simplify property transfers, reduce fraud, and increase transparency in real estate transactions.
Identity Management: Offer individuals greater control over their digital identities, enabling secure and verifiable access to services without relying on centralized databases.
The Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite its immense potential, blockchain technology is still evolving. Challenges include scalability issues (the speed at which transactions can be processed), regulatory uncertainties, and the energy consumption of some consensus mechanisms.
In Conclusion:
Blockchain is more than just a technological buzzword; it's a paradigm shift in how we establish trust and manage data in a digital world. By fostering transparency, security, and decentralization, it holds the key to unlocking new possibilities across industries, paving the way for a more trustworthy and efficient future. As we delve deeper into the digital age, understanding blockchain will be crucial for anyone looking to navigate the landscape of innovation.